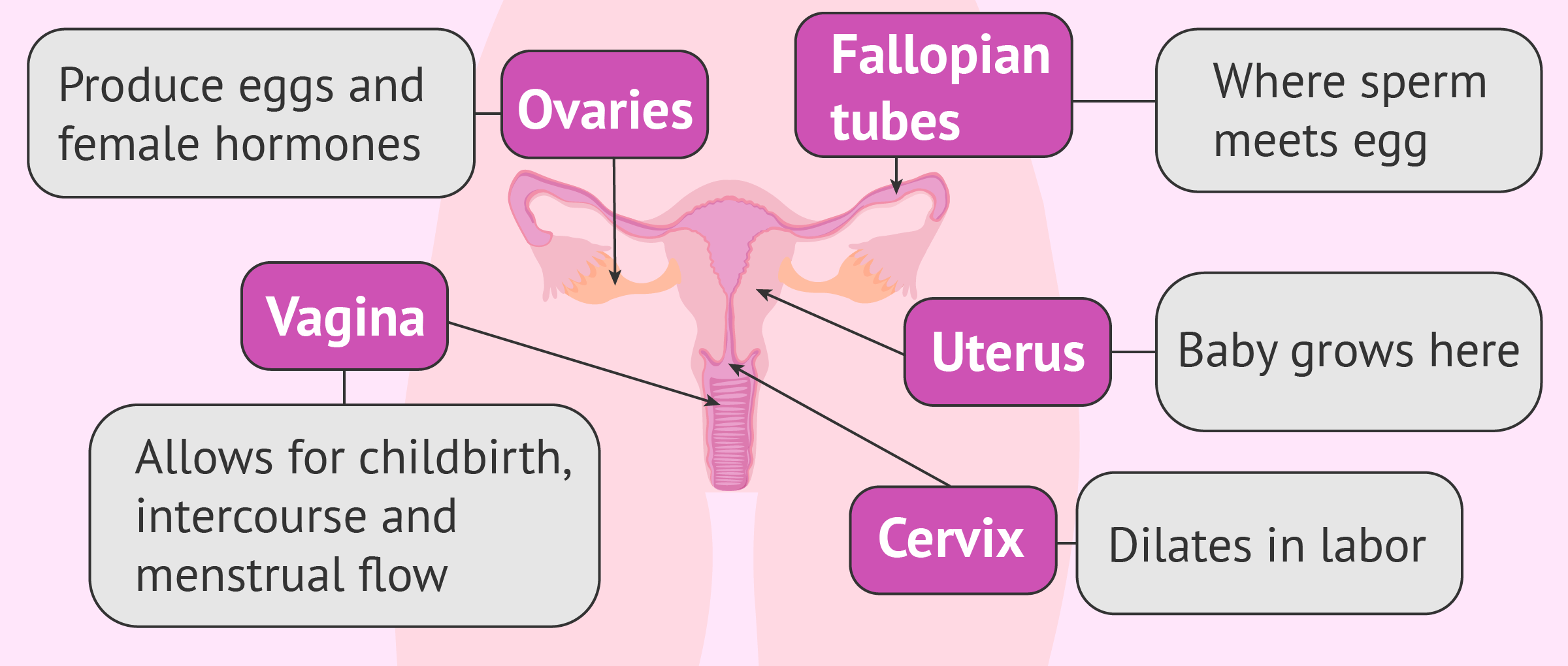
The matrix is a remarkable organ, primarily found in female mammals, and plays a key role in childbirth. It's a hollow structure located in the lower abdomen, accountable for nurturing a forming baby during gestational period. Beyond gestation, the uterus also sheds its inner lining during the period, which is a natural process in a woman's life. The contour is often inverted pear-like, and the organ can stretch considerably to accommodate a full-term baby.
Understanding The Ovaries
The ovaries are essential components of the woman's reproductive body, primarily responsible for producing oocytes and substances. Typically, females have two reproductive structures, found on either side of the uterus. They play a significant function throughout a female's life, starting with development during fetal stages and continuing through periods and possibly into this life phase. Their intricate functions are intimately intertwined with the general health and condition of a woman.
Understanding Fallopian {Tubes
Oviduct ducts are essential parts of the female reproductive system, playing a significant function in conception. They extend from the matrix to the ovaries, acting as a pathway for the oocyte to travel from the ovarium to the matrix. Often, fertilization takes place within the infundibulum, a particular section of the fallopian channel. Additionally, infection or a obstruction of these tubes can substantially influence the ability to conceive.
Keywords: vagina, vulva, anatomy, health, female, reproductive, intimate, hygiene, disorders, sexually transmitted infections, lubrication, childbirth, menstruation, pelvic floor, estrogen, pH balance, yeast infection, bacterial vaginosis, pelvic pain.
The Female Reproductive Area
The female anatomy is a remarkable part of the female reproductive structure, often confused with the vulva. It plays a critical role in childbirth, period flow, and romantic health. Proper hygiene is important for preventing problems like candidiasis, bacterial vaginosis, and addressing pelvic pain. Factors such as estrogen, vaginal acidity and adequate moistness significantly impact the woman's function. Awareness of STIs and their potential impact on the vagina is also absolutely necessary for overall sexual well-being. The strength of the muscles below the uterus is also important for recovery.
The Female Genitalia
The outer female reproductive structure encompasses the visible parts of the female’s genital region outside of the body. It's a complex structure with several functions, including shielding the inner structures and playing a function in reproductive function. Knowing its design is crucial for complete well-being and reproductive awareness. This includes the folds, clitoris, and the opening which houses the discharge port and genital entrance.
This Cervical Canal
The uterine neck, a crucial part of the female anatomy, acts as a gateway between the womb and the birth canal. Typically, it appears as a tight opening, about two to three units extended, and has a significant role in menstrual cycles and labor and delivery. In pregnancy, the cervix stays shut to shield the growing baby, and then dilates significantly to allow labor. This organ's condition is necessary for childbearing overall health.
Examining the Labia Majora
The labia majora are an pair of large skin structures that constitute part of the female sexual system. Often, they are similar to the pubic mound, being made up of adipose material and shrouded by pelvic fur, although this might vary widely among women. Acting as the important defensive wall, this assist to guard the additional delicate elements inside the vulva, and they contribute to the general form and performance of the female form.
Delving into Labia Minora
These minor labia are the pair of flexible folds within tissue located just inside the outer lips. This area change significantly in size, form, and shade among individuals, typically appear more pigmented than the adjacent skin. While this region don't a direct role for reproduction, they crucial for covering and delicate vaginal area. Alterations in these appearance or consistency might sometimes indicate the clinical condition, so it can be necessary to obtain medical counsel if some worries develop.
Understanding The Clitoris
Numerous people consider the clitoris, a minute organ situated at the front of the vulva, to be an crucial area regarding sexual enjoyment. Distinct from other reproductive organs, it lacks a direct purpose in conception; its primary function is connected with sexual feeling. The structure is remarkably sensitive, including thousands of nerve endings, enabling it to provide intense feelings. Additional investigation continues to increase our understanding of this complex anatomy and function.
- It is often known as the final erotic zone.
- Some consider understanding of the clitoris is often empowering.
Learning About Bartholin's Glands
Situated on both side of the birth opening, Bartholin's glands|glands|structures play a usually limited part in women's reproductive function. Usually, they produce a small amount of secretion|lubrication|moisture that aids with birth moistening during sexual activity. Rarely, these glands|ducts|tubes can get obstructed|clogged|swollen, leading to a uncomfortable cyst|swelling|mass and trouble with comfort. A condition, known as a Bartholin’s cyst, frequently requires doctor's treatment.
Okay, here's the article paragraph adhering to your strict spintax and HTML requirements, focusing on Skene's Glands.
Delving into Paraurethral {Glands
Skene's glands, also known as paraurethral glands, are accessory glands located near the urethra within the female's body. These structures play a role similarly to the male prostate structure, producing a fluid that contributes moistening and support of the urethra. Although their function isn't fully clear, research suggests these structures could play a role in female's genital function. A few women report painful issues related to the tubes, necessitating further study. To summarize, Skene’s glands represent an critical but often overlooked component of female internal structure.
Keywords: hymen, virginity, anatomy, female, membrane, health, misconception, folklore, cultural, biology, medical, intact, rupture, bleeding, hymenal, tissue, perception, history, examination, psychology.
The Hymeneal Tissue Explanation
The hymen is a thin fold of tissue located around the uterus in women. Often associated with chastity in societal perspectives, it's crucially a aspect of woman’s biology. It’s important to recognize that the hymen isn’t always intact, and its presence or absence doesn’t definitively reveal chastity. Many activities, including exercise, tampon use, or even strenuous coughing, can cause a break of the hymeneal tissue. The often-discussed discharge sometimes linked with hymeneal membrane tear is uncommon but isn’t always seen. Healthcare professionals should conduct an assessment of the hymen, but its appearance shouldn’t be interpreted as a sole measure of romantic history. There are many misconceptions surrounding the female tissue also it's vital to differentiate medical data from folklore and mental perceptions.
Okay, here's an article paragraph on "Perineum" adhering to your incredibly specific instructions.
Exploring the Perineum
The perineal region is the muscular region located anterior to the lower bowel and the vulva in males. It’s structure plays a important function in multiple physical activities, such as holding the pelvic tissues and assisting in tactile feedback. Additionally, it undergoes major distension during vaginal delivery in women, often can result in minor sensitivity. Knowing about this structure is thus crucial for medical experts.
Learning About Your Pelvic Floor
The pelvic floor is a group of tissues that support your bladder and have a significant role in bodily well-being. It's often overlooked, but toning your muscles can positively impact areas like sexual health to stability. Problems like incontinence or discomfort can sometimes are alleviated with specific training. It's beneficial investigating your pelvic area and how to support them functioning throughout your years.
The Vagina
The female canal, also known as the vagina, is a fibromuscular passage extending from the perineum to the uterine neck. It serves as the chief route for menstrual flow, sexual intercourse, and labor and delivery. This elastic structure is lined with tissue and possesses distinctive folds, called vertical ridges, which allow it to stretch considerably. Its length varies among individuals, but typically measures around 7-10 centimeters in resting state. Health of the birth passage is crucial for general health and comfort.
This Womb Membrane (Endometrium)
The endometrium is a remarkably responsive tissue that plays a crucial role in female reproductive function . This innermost layer of the uterus sheds during menstruation if pregnancy doesn’t happen , and it thickens each month in anticipation for a potential lodging of a fertilized ovum . It’s made up of secretory and stroma cells, creating a unique environment that constantly modifies throughout the reproductive cycle. Furthermore , the endometrial depth and structure are significantly shaped by hormones , primarily oestrogen and progesterone .
Understanding Egg Follicles
Female follicles are critical structures within the uterus, playing a key role in the growth of eggs and the maintenance of the menstrual cycle. Each uterus initially contains a large number of primordial follicles, which are immature sacs surrounding immature ova. Throughout a woman's fertility period, these follicles progress through different stages, some experiencing a maturation process, others staying in a inactive state. The course of follicle maturation involves intricate interactions between signals, including FSH and ovarian hormones, which guide the events leading to reproduction.
Understanding Oestrogen Receivers
Estrogen receptors are intracellular structures found within multiple cell sorts throughout the body. These significant components act as controllers, binding to oestrogen hormones and subsequently triggering a cascade of cellular events. Basically, when an oestrogen chemical binds to a receptor, it encourages a structural modification that leads to different gene activity, influencing various functions, such as growth, reproduction, and general well-being. The presence and concentration of these receivers can vary significantly across tissues, justifying the wide-ranging effects of estrogen in the human structure.
Estrous Receptors
Progesterone receptors, often abbreviated as PRs, are intracellular check here proteins that mediate the actions of progesterone, a crucial steroid chemical. These proteins constitute the nuclear receptor superfamily and, upon binding with progesterone, undergo a conformational change leading to translocation to the core and subsequent control of gene transcription. Two major variations, PR-A and PR-B, occur due to alternative modification of the genetic material, each exhibiting subtly distinct influencing properties and tissue distribution. Their function is paramount in the establishment of gestation, the progression of the mammary glands, and the timing of the ovulatory cycle in females. Dysregulation of pregnancy receptor signaling has been linked in a number of reproductive disorders.
Keywords: reproductive system, male reproductive system, female reproductive system, fertilization, hormones, ovaries, testes, uterus, sperm, egg, menstruation, puberty, pregnancy, contraception
Our Reproductive System
The human reproductive system is a intricate network of components responsible for procreation . It broadly splits into the male reproductive system and the female reproductive system, each with distinct functions. In males, the testes produce sperm, while in females, the ovaries release eggs. Fertilization, the joining of a sperm and an egg, can lead to pregnancy, a incredible period of growth. Hormones, like estrogen and testosterone, play a critical role in regulating development during puberty and throughout reproductive life. Menstruation is a cyclical process in females, and contraception methods are obtainable to avoid unintended pregnancies. This amazing system is key to the perpetuation of our kind .